Esophagus
Esophagus Surgeon in Nagpur Maharashtra.
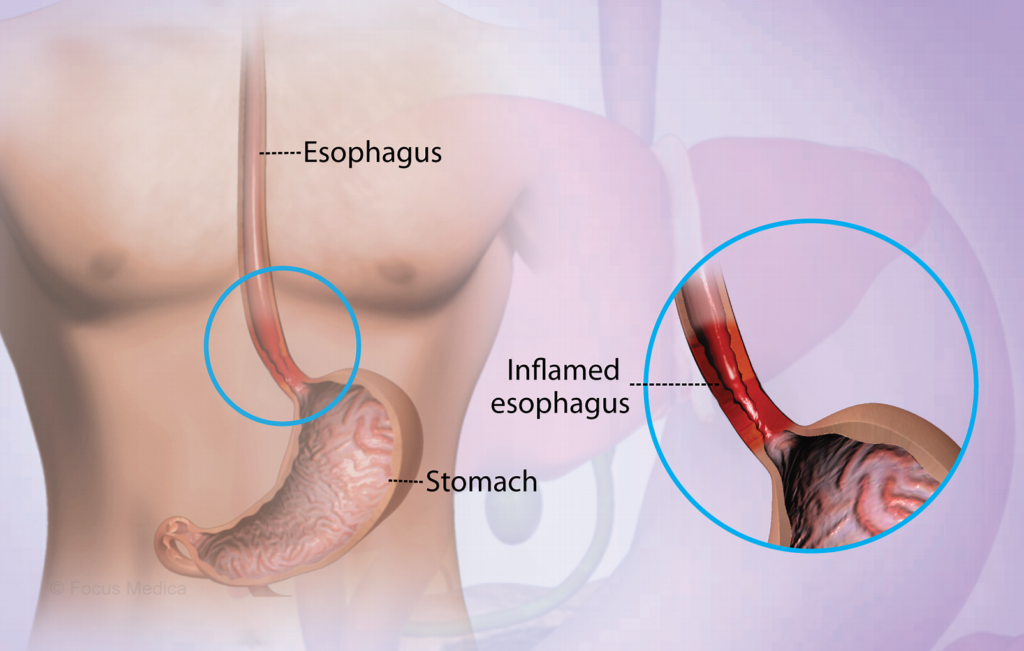
Dr. Manish Upwanshi is one of the FAMOUS Esophagus Surgeons in Nagpur City. Esophagitis is an inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the throat to the stomach. If left untreated, this condition can become very uncomfortable, causing problems with swallowing, ulcers, and scarring of the esophagus.
The esophagus is located in the center of your chest in an area called the mediastinum. It lies behind your windpipe (trachea) and in front of your spine. The average adult esophagus is about 10 to 13 inches long. It’s about three-fourths of an inch thick at its smallest point.
Esophagitis Symptoms
Symptoms of esophagitis include:
- Difficult or painful swallowing
- Acid reflux
- Heartburn
- A feeling of something of being stuck in the throat
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
If you have any of these symptoms, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible.
What problems and conditions can affect the esophagus?
The most common problem that can affect your esophagus is acid reflux. Acid reflux occurs when your lower esophageal sphincter opens when it’s not supposed to. This allows stomach acid and digestive juices to flow back from your stomach into your esophagus. This can cause inflammation and heartburn.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a more severe form of acid reflux. With GERD, stomach acid persistently flows back into your esophagus. Besides heartburn, some people develop a cough, chest pain, hoarseness, bad breath and/or trouble swallowing. You may feel like there’s a lump in the back of your throat. Over time, GERD can cause significant damage to your esophagus.
Other problems that can affect your esophagus include:
- Achalasia: Achalasia is a rare disorder in which your lower esophageal sphincter doesn’t open when it’s supposed to. This prevents food from getting into your stomach.
- Esophageal diverticulum: An esophageal diverticulum is a pouch that bulges outward in a weak section of your esophageal lining. You may be unable to swallow if the diverticulum causes an obstruction.
- Esophageal varices: Esophageal varices are large or swollen veins on the lining of your esophagus. Varices can be fatal if they break open and bleed.
- Esophagitis: Esophagitis is inflammation and irritation of the lining of your esophagus. Acid reflux, infection, vomiting, certain medications or radiation treatment may cause esophagitis.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis: A buildup of certain white blood cells called eosinophils in your esophagus causes this type of esophagitis. Food allergies may cause the buildup of eosinophils in your esophagus.
- Barrett’s esophagus: Barrett’s esophagus is a change in the tissue lining your lower esophagus. Long-term (chronic) GERD may cause the change. Barrett’s esophagus can increase your risk of getting esophageal cancer.
Rarely, esophageal cancer can occur. Two types of cancer can develop in your esophagus:
- Adenocarcinoma: This type of cancer usually develops in the lower part of your esophagus. It starts in the cells that make mucus (gland cells). Adenocarcinoma commonly develops from Barrett’s esophagus.
- Squamous cell carcinoma: This type of cancer develops in the cells that line your esophagus. It usually affects the upper and middle parts of your esophagus.
How do you fix esophagus problems?
Treatment for esophagus problems depends on the cause. Some esophagus problems can be treated with over-the-counter medication or diet changes. Other conditions may require prescription medication, procedures or surgery.
